Hi, this CodeIgniter Bootstrap Tutorial will teach you How to Insert Form Data into MySQL Database using CodeIgniter, Bootstrap CSS framework and jQuery UI. I'm going to walk you through step-by-step, creating a form in codeigniter and insert those form data into database. To design the said php codeigniter form, we use twitter boostrap css framework and it's one of my all time favorite and saves time from creating style sheets of our own. If you wonder how to use bootstrap in codeigniter, then read this tutorial on Integrating Bootstrap with CodeIgniter.
MySQL Database Example
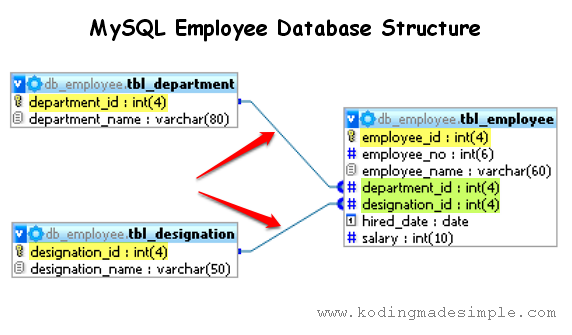
I'm going to use mysql database as an example for this tutorial. Here, take a look at the sample employee database I have.
The fields that are highlighted in yellow color are primary keys and those ones in green are foreign keys.
Now run this sql query in mysql to create the above database.
SET SQL_MODE="NO_AUTO_VALUE_ON_ZERO";
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `tbl_department` (
`department_id` int(4) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`department_name` varchar(80) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`department_id`)
) ENGINE=MyISAM DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1 AUTO_INCREMENT=6 ;
INSERT INTO `tbl_department` (`department_id`, `department_name`) VALUES
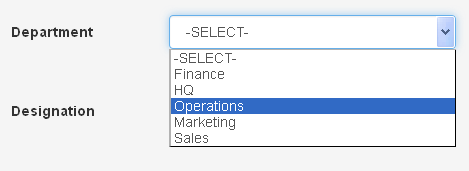
(1, 'Finance'),
(2, 'HQ'),
(3, 'Operations'),
(4, 'Marketing'),
(5, 'Sales');
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `tbl_designation` (
`designation_id` int(4) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`designation_name` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`designation_id`)
) ENGINE=MyISAM DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1 AUTO_INCREMENT=6 ;
INSERT INTO `tbl_designation` (`designation_id`, `designation_name`) VALUES
(1, 'VP'),
(2, 'Manager'),
(3, 'Executive'),
(4, 'Trainee'),
(5, 'Senior Executive');
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `tbl_employee` (
`employee_id` int(4) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`employee_no` int(6) NOT NULL,
`employee_name` varchar(60) NOT NULL,
`department_id` int(4) NOT NULL,
`designation_id` int(4) NOT NULL,
`hired_date` date NOT NULL,
`salary` int(10) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`employee_id`)
) ENGINE=MyISAM DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1 AUTO_INCREMENT=6 ;
Recommended Read: How to Connect to Multiple Databases in CodeIgniter
The Model ('models/employee_model.php')
First create the model file 'employee_model.php' with two functions. One is to fetch all the records from department table and other one to fetch all the records from the designation table.
<?php
/*
* File Name: employee_model.php
*/
if ( ! defined('BASEPATH')) exit('No direct script access allowed');
class employee_model extends CI_Model
{
function __construct()
{
// Call the Model constructor
parent::__construct();
}
//get department table to populate the department name dropdown
function get_department()
{
$this->db->select('department_id');
$this->db->select('department_name');
$this->db->from('tbl_department');
$query = $this->db->get();
$result = $query->result();
//array to store department id & department name
$dept_id = array('-SELECT-');
$dept_name = array('-SELECT-');
for ($i = 0; $i < count($result); $i++)
{
array_push($dept_id, $result[$i]->department_id);
array_push($dept_name, $result[$i]->department_name);
}
return $department_result = array_combine($dept_id, $dept_name);
}
//get designation table to populate the designation dropdown
function get_designation()
{
$this->db->select('designation_id');
$this->db->select('designation_name');
$this->db->from('tbl_designation');
$query = $this->db->get();
$result = $query->result();
$designation_id = array('-SELECT-');
$designation_name = array('-SELECT-');
for ($i = 0; $i < count($result); $i++)
{
array_push($designation_id, $result[$i]->designation_id);
array_push($designation_name, $result[$i]->designation_name);
}
return $designation_result = array_combine($designation_id, $designation_name);
}
}
?>
Populate the Drop Down List from Database in CodeIgniter Form
If you wonder why we need to fetch data from the above said tables, well the employee table consists of two dependant fields department_id and designation_id for which their values should be derived from tbl_department and tbl_designation respectively. So in our codeigniter form, we should use dropdown list pre-populated with the list of available department and designation names like this.
The Controller ('controllers/employee.php')
Next create the controller file 'employee.php' and load the required libraries and helpers.
<?php
/*
* File Name: employee.php
*/
if ( ! defined('BASEPATH')) exit('No direct script access allowed');
class employee extends CI_Controller
{
public function __construct()
{
parent::__construct();
$this->load->library('session');
$this->load->helper('form');
$this->load->helper('url');
$this->load->database();
$this->load->library('form_validation');
//load the employee model
$this->load->model('employee_model');
}
?>
We require the 'database' library as we have to connect and fetch and insert data into database. Also loaded the session library for displaying notification. Learn more about using codeigniter sessions in our tutorial create login form in codeigniter and bootstrap.
Note: When developing a complete codeigniter application, you have to load the session library in each and every controller module for which you want only the logged in user to access.
Next add index() function which is the default function of any codeigniter controllers. As I have mentioned earlier we have to populate the drop down list in the view with values from database. It's time to callback our employee model functions to fetch the department and designation table data.
<?php
//index function
function index()
{
...
//fetch data from department and designation tables
$data['department'] = $this->employee_model->get_department();
$data['designation'] = $this->employee_model->get_designation();
}
?>
Add CodeIgniter Form Validation Rules
Next we have to validate the form input data posted by the user for database insert. Using the codeigniter form validation library, let's set the required validation rules for each and every field present in our employee form.
<?php
//index function
function index()
{
...
//set validation rules
$this->form_validation->set_rules('employeeno', 'Employee No', 'trim|required|numeric');
$this->form_validation->set_rules('employeename', 'Employee Name', 'trim|required|xss_clean|callback_alpha_only_space');
$this->form_validation->set_rules('department', 'Department', 'callback_combo_check');
$this->form_validation->set_rules('designation', 'Designation', 'callback_combo_check');
$this->form_validation->set_rules('hireddate', 'Hired Date', 'required');
$this->form_validation->set_rules('salary', 'Salary', 'required|numeric');
}
?>
Add Custom Form Validation Callback in CodeIgniter
Next create two codeingiter custom validation callback functions, one to make sure the user selects valid department and designations in the drop down list and the other one to restrict the employee name field to contain only alphabets and space.
<?php
//custom validation function for dropdown input
function combo_check($str)
{
if ($str == '-SELECT-')
{
$this->form_validation->set_message('combo_check', 'Valid %s Name is required');
return FALSE;
}
else
{
return TRUE;
}
}
//custom validation function to accept only alpha and space input
function alpha_only_space($str)
{
if (!preg_match("/^([-a-z ])+$/i", $str))
{
$this->form_validation->set_message('alpha_only_space', 'The %s field must contain only alphabets or spaces');
return FALSE;
}
else
{
return TRUE;
}
}
?>
Run Form Validation on CodeIgniter Bootstrap Form Data
Next we run the form validation on the form data we received upon submission. If the submitted form contains valid data then we insert the form data into database else display the error message in the codeigniter view. Add this code to controller's index() function.
<?php
//index function
function index()
{
...
if ($this->form_validation->run() == FALSE)
{
//fail validation
$this->load->view('employee_view', $data);
}
else
{
//pass validation
$data = array(
'employee_no' => $this->input->post('employeeno'),
'employee_name' => $this->input->post('employeename'),
'department_id' => $this->input->post('department'),
'designation_id' => $this->input->post('designation'),
'hired_date' => @date('Y-m-d', @strtotime($this->input->post('hireddate'))),
'salary' => $this->input->post('salary'),
);
//insert the form data into database
$this->db->insert('tbl_employee', $data);
//display success message
$this->session->set_flashdata('msg', '<div class="alert alert-success text-center">Employee details added to Database!!!</div>');
redirect('employee/index');
}
}
?>
As you can see in the above code, codeigniter provides very easy way of running form validations. Upon setting the validation rules we have to run $this->form_validation->run() statement, which will return true if all our validation rule passes else returns false. In case of failure, we reload the form and display the corresponding error messages in the view.
On successful validation check, we get all the form field values in an array and insert into database using the codeigniter statement, $this->db->insert('tbl_employee', $data). The first parameter of the insert() function should be the database table name and the second parameter is of an array of field name and their values. As you can see above, I have converted the date format into 'Y-m-d' with the date() function because mysql uses the very same date format. If you try to insert date in some other format, then the provided date will not be properly inserted into mysql.
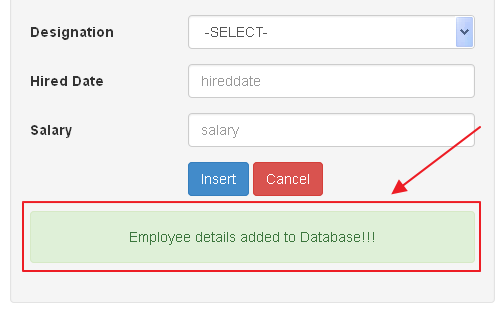
After inserting into database we should display some sort of notification for which we use $this->session->set_flashdata(). The flashdata() will display the message immediately after page redirection.
Here is the complete code for the controller file.
<?php
/*
* File Name: employee.php
*/
if ( ! defined('BASEPATH')) exit('No direct script access allowed');
class employee extends CI_Controller
{
public function __construct()
{
parent::__construct();
$this->load->library('session');
$this->load->helper('form');
$this->load->helper('url');
$this->load->database();
$this->load->library('form_validation');
//load the employee model
$this->load->model('employee_model');
}
//index function
function index()
{
//fetch data from department and designation tables
$data['department'] = $this->employee_model->get_department();
$data['designation'] = $this->employee_model->get_designation();
//set validation rules
$this->form_validation->set_rules('employeeno', 'Employee No', 'trim|required|numeric');
$this->form_validation->set_rules('employeename', 'Employee Name', 'trim|required|xss_clean|callback_alpha_only_space');
$this->form_validation->set_rules('department', 'Department', 'callback_combo_check');
$this->form_validation->set_rules('designation', 'Designation', 'callback_combo_check');
$this->form_validation->set_rules('hireddate', 'Hired Date', 'required');
$this->form_validation->set_rules('salary', 'Salary', 'required|numeric');
if ($this->form_validation->run() == FALSE)
{
//fail validation
$this->load->view('employee_view', $data);
}
else
{
//pass validation
$data = array(
'employee_no' => $this->input->post('employeeno'),
'employee_name' => $this->input->post('employeename'),
'department_id' => $this->input->post('department'),
'designation_id' => $this->input->post('designation'),
'hired_date' => @date('Y-m-d', @strtotime($this->input->post('hireddate'))),
'salary' => $this->input->post('salary'),
);
//insert the form data into database
$this->db->insert('tbl_employee', $data);
//display success message
$this->session->set_flashdata('msg', '<div class="alert alert-success text-center">Employee details added to Database!!!</div>');
redirect('employee/index');
}
}
//custom validation function for dropdown input
function combo_check($str)
{
if ($str == '-SELECT-')
{
$this->form_validation->set_message('combo_check', 'Valid %s Name is required');
return FALSE;
}
else
{
return TRUE;
}
}
//custom validation function to accept only alpha and space input
function alpha_only_space($str)
{
if (!preg_match("/^([-a-z ])+$/i", $str))
{
$this->form_validation->set_message('alpha_only_space', 'The %s field must contain only alphabets or spaces');
return FALSE;
}
else
{
return TRUE;
}
}
}
?>
The View ('views/employee_view.php')
The codeigniter view is the interface between the application and the user and contains the html markup for our employee form.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>CodeIgniter | Insert Employee Details into MySQL Database</title>
<!--link the bootstrap css file-->
<link href="<?php echo base_url("assets/bootstrap/css/bootstrap.css"); ?>" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" />
<!-- link jquery ui css-->
<link href="<?php echo base_url('assets/jquery-ui-1.11.2/jquery-ui.min.css'); ?>" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" />
<!--include jquery library-->
<script src="<?php echo base_url('assets/js/jquery-1.10.2.js'); ?>"></script>
<!--load jquery ui js file-->
<script src="<?php echo base_url('assets/jquery-ui-1.11.2/jquery-ui.min.js'); ?>"></script>
<style type="text/css">
.colbox {
margin-left: 0px;
margin-right: 0px;
}
</style>
<script type="text/javascript">
//load datepicker control onfocus
$(function() {
$("#hireddate").datepicker();
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-sm-offset-3 col-lg-6 col-sm-6 well">
<legend>Add Employee Details</legend>
<?php
$attributes = array("class" => "form-horizontal", "id" => "employeeform", "name" => "employeeform");
echo form_open("employee/index", $attributes);?>
<fieldset>
<div class="form-group">
<div class="row colbox">
<div class="col-lg-4 col-sm-4">
<label for="employeeno" class="control-label">Employee No</label>
</div>
<div class="col-lg-8 col-sm-8">
<input id="employeeno" name="employeeno" placeholder="employeeno" type="text" class="form-control" value="<?php echo set_value('employeeno'); ?>" />
<span class="text-danger"><?php echo form_error('employeeno'); ?></span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<div class="row colbox">
<div class="col-lg-4 col-sm-4">
<label for="employeename" class="control-label">Employee Name</label>
</div>
<div class="col-lg-8 col-sm-8">
<input id="employeename" name="employeename" placeholder="employeename" type="text" class="form-control" value="<?php echo set_value('employeename'); ?>" />
<span class="text-danger"><?php echo form_error('employeename'); ?></span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<div class="row colbox">
<div class="col-lg-4 col-sm-4">
<label for="department" class="control-label">Department</label>
</div>
<div class="col-lg-8 col-sm-8">
<?php
$attributes = 'class = "form-control" id = "department"';
echo form_dropdown('department',$department,set_value('department'),$attributes);?>
<span class="text-danger"><?php echo form_error('department'); ?></span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<div class="row colbox">
<div class="col-lg-4 col-sm-4">
<label for="designation" class="control-label">Designation</label>
</div>
<div class="col-lg-8 col-sm-8">
<?php
$attributes = 'class = "form-control" id = "designation"';
echo form_dropdown('designation',$designation, set_value('designation'), $attributes);?>
<span class="text-danger"><?php echo form_error('designation'); ?></span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<div class="row colbox">
<div class="col-lg-4 col-sm-4">
<label for="hireddate" class="control-label">Hired Date</label>
</div>
<div class="col-lg-8 col-sm-8">
<input id="hireddate" name="hireddate" placeholder="hireddate" type="text" class="form-control" value="<?php echo set_value('hireddate'); ?>" />
<span class="text-danger"><?php echo form_error('hireddate'); ?></span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<div class="row colbox">
<div class="col-lg-4 col-sm-4">
<label for="salary" class="control-label">Salary</label>
</div>
<div class="col-lg-8 col-sm-8">
<input id="salary" name="salary" placeholder="salary" type="text" class="form-control" value="<?php echo set_value('salary'); ?>" />
<span class="text-danger"><?php echo form_error('salary'); ?></span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-sm-offset-4 col-lg-8 col-sm-8 text-left">
<input id="btn_add" name="btn_add" type="submit" class="btn btn-primary" value="Insert" />
<input id="btn_cancel" name="btn_cancel" type="reset" class="btn btn-danger" value="Cancel" />
</div>
</div>
</fieldset>
<?php echo form_close(); ?>
<?php echo $this->session->flashdata('msg'); ?>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
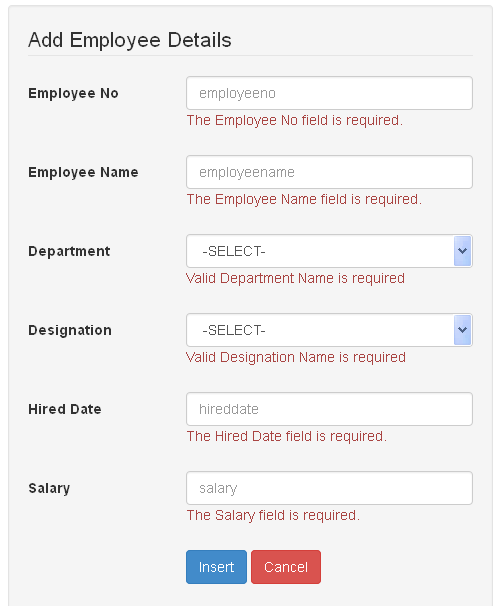
This is how our employee form looks like.
As already said, I have used twitter bootstrap css framework with codeigniter to design this user input form. Bootstrap provides all the necessary css components to design a website and let you jump start immediately into application development without worrying about the stylesheet. Here are some of our codeigniter tutorials for you which uses Twitter Bootstrap framework for front end development.
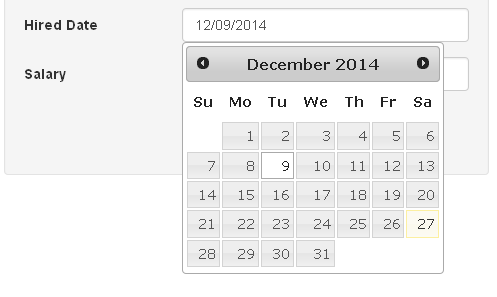
Add Date Picker to CodeIgniter Form using jQuery UI
The employee form contains a date input field named 'hired date'. To enhance the user experience, I have used jQuery UI plug-in to add date picker calendar. And this date picker calendar pops up when the 'hired date' input field got focus and let the user to pick up the date without typing.
To add the date picker control to codeigniter form with jquery ui plug-in add the javascript line,
$("#hireddate").datepicker();
"#hireddate" is the form element id. To add date picker to more than one input field, use comma (,) to separate the id's like this $("#id1, #id2, #id3").datepicker();
Also using echo form_error() below every input element will display the corresponding form validation error messages under the input elements like this.
The functions form_open() and form_close() are used to add html form element to the codeigniter view. Finally the line echo $this->session->flashdata('msg') displays the success message when the form values are inserted into database without error.
Also Read:
Hope you have liked this CodeIgniter Database Tutorial on inserting form data into database. If you want to learn the complete basics of the framework, then check this guide on codeigniter beginners tutorial.